KIDNEYS
What are the Kidneys?
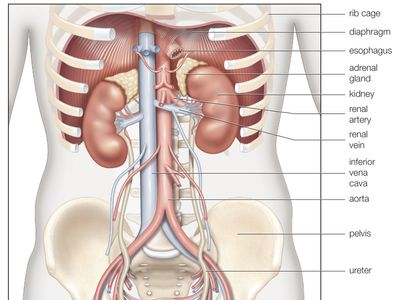
The kidneys play key roles in body function, not only by filtering the blood and getting rid of waste products, but also by balancing levels of electrolytes in the body, controlling blood pressure. and stimulating the production of red blood cells. The blood supply to your kidneys enables them to do the following tasks:
• Regulate the composition of your blood
• Keep the concentrations of various ions and other important substances constant • Keep the volume of water in your body constant
• Remove wastes from your body (urea. ammonia, drugs, toxic substances)
• Keep the acid/base concentration of your blood constant
• Help regulate your blood pressure
• Stimulate the making of red blood cells
• Maintain your body’s calcium levels
The kidneys have the ability to monitor the amount of body fluid, the concentrations of electrolytes like soctium and potassium, and the acid-base balance of the body. They filter waste products of body metabolism, like urea from protein metabolism and uric acid from DNA breakdown. Two waste products in the blood can be measured: blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (Cr).
When blood flows to the kidney, sensors within the kidney decide how much water to excrete as urine, along with what concentration of electrolytes. For example, if a person is dehydrated from exercise or from an illness, the kidneys will hold onto as much water as possible and the urine becomes very concentrated,when adequate water is present in the body, the urine is much more dilute, and the urine becomes clear. This system is controlled by renin, a hormone produced in the kidney that is part of the fluid and blood pressure regulation systems of the body.
Kidneys are also the source of erythropoietin in the body, a hormone that stimulates the bone marrow to make red blood cells. Special cells in the kidney monitor the oxygen concentration in blood. If oxygen levels fall, erythropoietin levels rise and the body starts to manufacture more red blood cells. After the kidneys filter blood, the urine is excreted through the ureter, a thin tube that connects it to the bladder. It is then stored in the bladder awaiting urination. Medications: Some medications are toxic to the kidney, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen. Others are antibiotics like aminoglycosides krantamicin (Garamycin), tobramvcin) lithium (Eskalith. Lithobid), iodine-containing methcations such as those injected for rathology dye studies.


