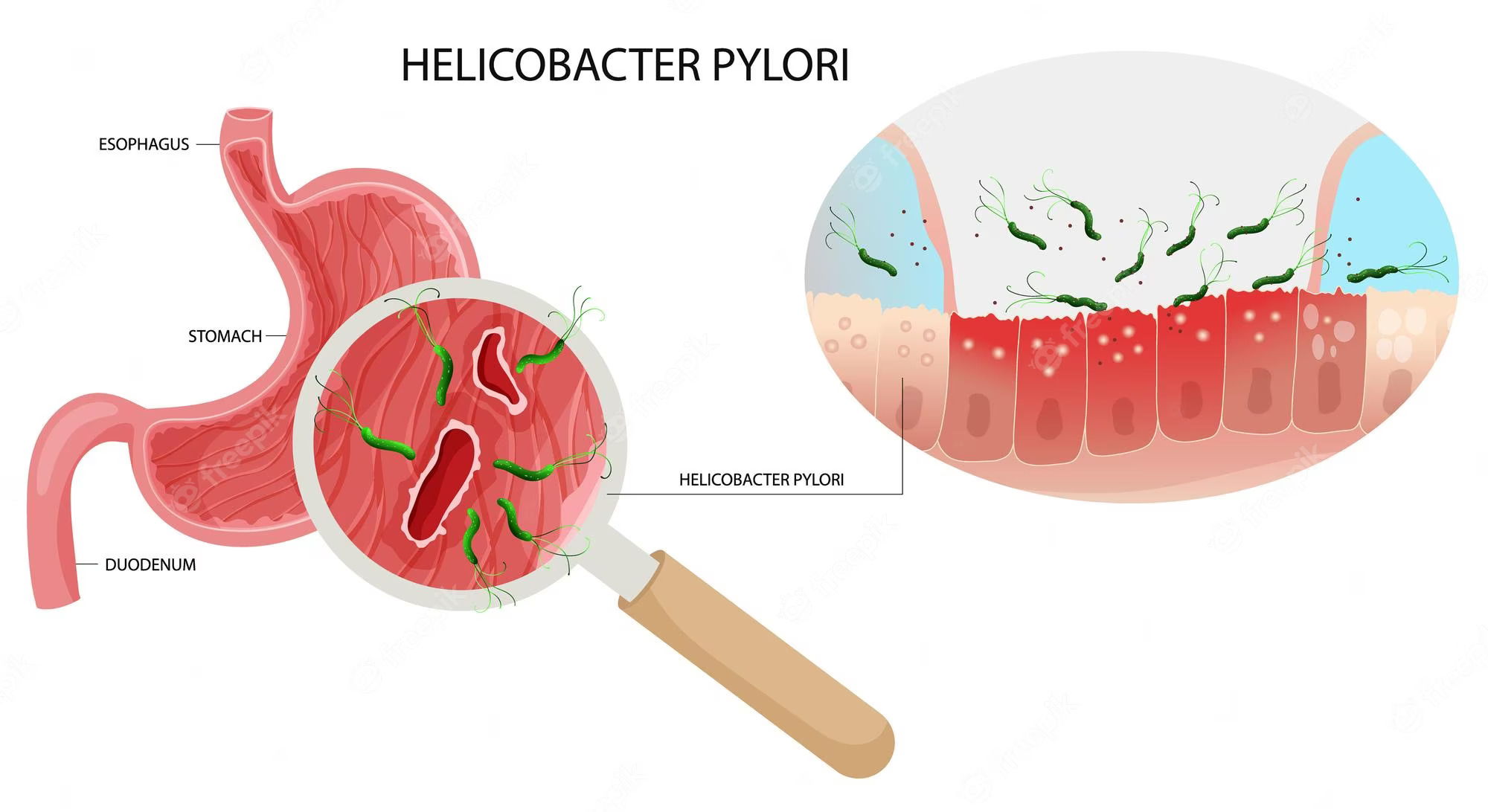
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacterial infection that primarily affects the stomach lining. This common infection is known to cause a range of gastrointestinal issues, including gastritis, and peptic ulcers, and even increase the risk of stomach cancer. Understanding the treatment options available for Helicobacter pylori infection treatment is essential for managing its symptoms and preventing potential complications. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the various strategies for treating Helicobacter pylori infection.
Helicobacter pylori Treatment generally involves a combination of antibiotics and other medications to eradicate the bacteria and promote healing of the stomach lining. The choice of treatment may depend on factors such as the severity of the infection, the presence of complications, and the patient’s medical history. Here are the key approaches to treating H. pylori infection:
Triple therapy is a common treatment approach that involves taking three different medications simultaneously for about 10 to 14 days. This combination typically includes:
Quadruple therapy, also known as “concomitant therapy,” involves taking four medications at the same time:
Quadruple therapy is often recommended when there is a concern about antibiotic resistance or if the initial treatment fails.
Sequential therapy is another approach that involves taking two sets of antibiotics in sequence, followed by a PPI. This strategy aims to exploit the vulnerabilities of H. pylori by exposing it to different antibiotics at different stages of its life cycle.
In cases where other treatments fail or when antibiotic resistance is suspected, levofloxacin-based therapy may be considered. Levofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that targets H. pylori.
Tailored therapy involves conducting tests to determine the specific antibiotics to which the H. pylori bacteria are susceptible. This personalized approach ensures that the chosen antibiotics are more likely to be effective.
After completing the prescribed treatment regimen, it’s important to undergo follow-up testing to confirm the eradication of the bacteria. This usually involves a breath test, stool test, or endoscopy with biopsy.
While medications are essential for Helicobacter pylori treatment, certain lifestyle modifications can complement the treatment process and promote healing. These include:
To prevent recurrence of Helicobacter pylori infection, it’s important to adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen and follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Additionally, practicing good hygiene and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can play a role in preventing reinfection.
Helicobacter pylori infection is a prevalent condition that can have wide-ranging effects on gastrointestinal health. Timely and appropriate Helicobacter pylori treatment is crucial for managing symptoms, preventing complications, and promoting overall well-being. If you suspect you have an H. pylori infection or are experiencing symptoms such as abdominal pain, indigestion, or discomfort, seek medical attention. A healthcare provider can diagnose the infection, recommend suitable treatment options, and guide you toward a path of relief and recovery. Remember that early intervention and adherence to treatment are key factors in effectively managing H. pylori infection and restoring your digestive health.